Table of Contents
More and more, you get competition in mainly all the industries. It can appear at almost anytime. Brands and businesses fight hard to differentiate themselves from others and get a big share of the market or just attract users towards them. Some succeed in doing so, and some others don’t. Today I would like to talk about a term that was created to distinguish the design & the thinking that happens behind this “surface”: Design thinking.
Lately we’ve noticed that huge companies have been getting beaten by startups, or quite young companies. Have you ever wondered how is it that a small team, with not even 5% of the resources that huge players have, end up getting bigger than those, just in a few years?
In my opinion (and many others), those huge brands haven’t been able to really adapt and realise that instead of always trying to exploit this business model that they’ve had working for a while, they should maybe start spending resources on innovation. On digital transformation. On creativity. On re-inventing instead of doing the same old thing they do.
So what is design thinking?
Design thinking is a methodology that is followed in order to solve complex problems, focusing on providing a solution to the user/client.
This solution focused approach helps to develop solutions that are human centered. It’s in fact a customer centric process that is based on creating an outcome that will add value to the user by responding to his needs. It’s about creating a business strategy that will translate into a value for the customer as well as a market opportunity.
The process takes into account human emotions and is mainly based on logic, high imagination and intuition enabling you to create ideas that are innovative and that will respond to unmet needs through emerging technologies.
So yes, it’s about playing with those three aspects: the possibilities that are given by technology itself, the requirements to have a successful business and the customer’s needs that has to be fulfilled.
The fact that the word design is used doesn’t imply that design thinking is about the design industry. Actually, design thinking can be applied to any industry; we could be using it for the development of new products, of new services, of improved processes, etc.
The idea is to discover, through observations what the actual processes are, where the user is, what are his needs? Brainstorm in teams to solve the problem, find a solution. Prototype. Test it. Improve and improve more through iterations.
Closer look at the design thinking process
We just went over a few design thinking definitions and got a pretty good idea of what it is. But I believe that it all gets clearer once we understand the process, once we’re able to get more details about this methodology. So here’s a summarised version of the design thinking process that is broken up into a 5 step iterative process.
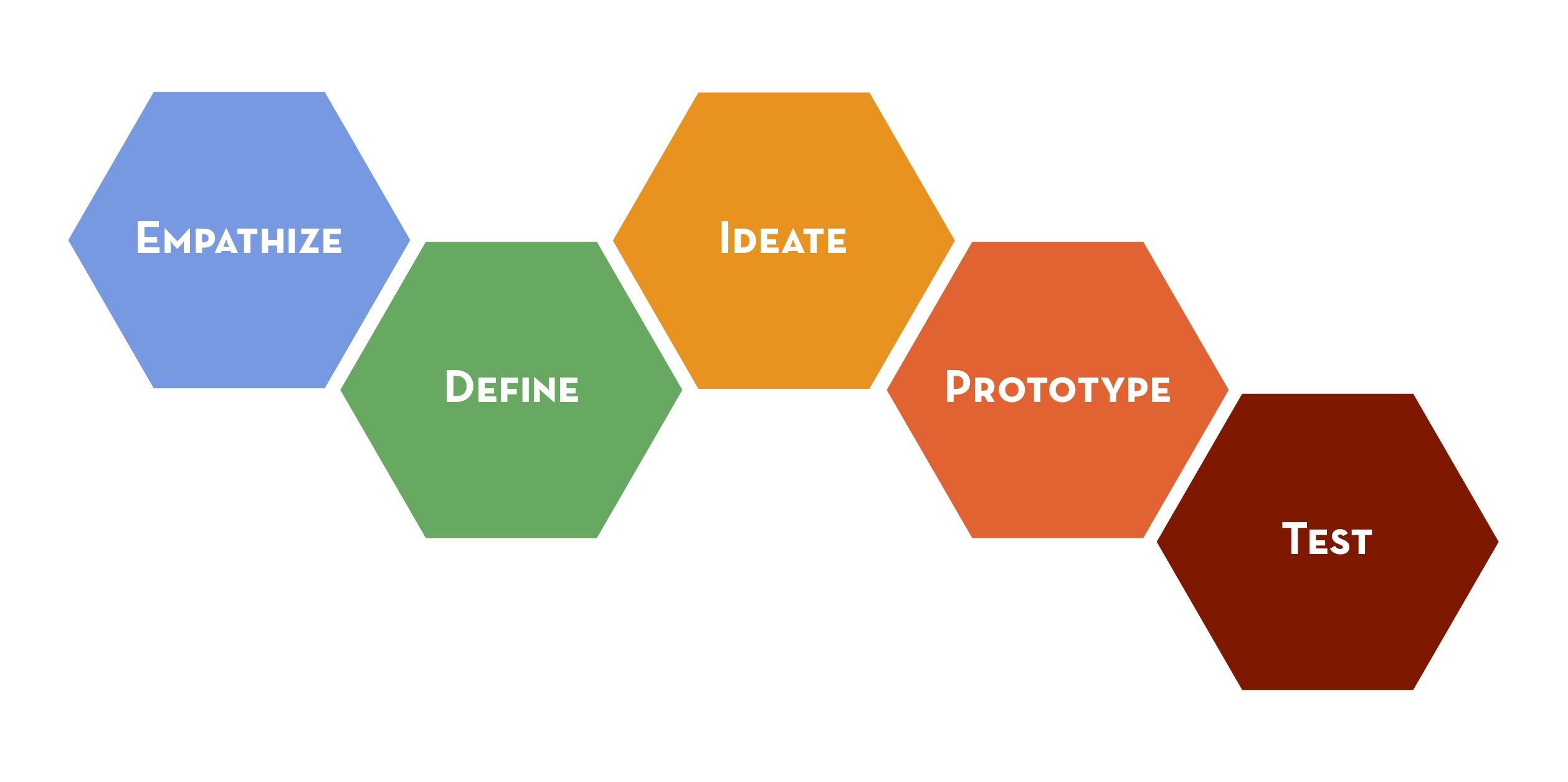
Empathise
As I said earlier, it’s a human-centered process, which means that understanding people we are designing for is crucial. In fact to be able to design for someone, you need to understand him. The empathising phase is about trying to understand how users do things, why they do it, the logic behind, the needs (let them be physical or emotional) their thoughts, what is important for them, what they might like, etc.
We start off by observing the user, always in a relevant context of course, and try to capture a gap between what he says and what he really does. Find actions he does but that he doesn’t mention. Pure observation.
After that, we get to the deeper part which consists in asking questions, talking, and specially let the other talk and develop. A great tip here is to always ask why. This helps you get a better understanding, something deeper and more relevant. Finally, we ask the target to pass to action. Do the task physically and explain what he is doing and the reason behind, why is he doing what he’s doing.
Define
After all the observation done and after all the insights that we got about the user, we need to make sense out of it. In other words, define the problem we are going to address. In fact, we need to give our point of view about the situation because this will enable us to choose the right solution to this challenge. So we build this sort of “mission statement” that will represent the insights we got to solve user needs. The idea is to get the right problem.
Ideate
Here, we’re mainly talking about brainstorming. We want to expose all the options possible, get as much ideas as we can. The idea is not to get the best idea, we want to get many options that we will verify and test afterwards.
No barriers needed, free your creativity, let your mind go, that’s when innovative solutions come out. Let ideas flow, jumping from one to another, you never know where you will end up, and that’s the beauty of it.
Prototype
In the prototype phase, what’s interesting is that you build possible solutions that are quick and cheap to build, in order to see if it really is the right solution, through feedback regarding this prototype. The idea is that the user uses this prototype, tries it out, lives it and feels it.
This helps us watch reactions at an early stage and see how they can interact with it and “test” it. Just hearing or watching a solution can bring some insights but it won’t be as efficient than really trying it. If it fails, it’s ok, we only got more information on what doesn’t work, and it didn’t cost much, we’re one step closed to the real thing!
As always, this is a user centred design, never forgot why the prototype is being built and to whom. Many people do the error to spend too much time on a prototype, and this is against the concept! Just go for it, quickly, build something and try it quickly and learn!
Test
After building the prototype, we want to know what are the outcomes. That’s the test stage. Here we get the chance to understand the users even better, we get some feedback, we see how they interacted with the feedback, what they think, how they felt using it. Don’t forget the Why question strategy! Yes or no is never enough. Make the testing stage realistic, test it in the real environment of the user, they should feel confortable and not feel any sort of pressure on them. You shouldn’t tell them what to do, it’s better to see how they do it following their intuition. The idea is to do as many iterations as possible until you reach perfection, sometimes you will have to go back to scratch and other times you will only need to change things to the prototype. In all the situations, it’s an advancement. You’re going forward.
Competitive advantage through creativity & innovation
Design thinking at school
Is it really important at school? I believe it is. That’s where we all start, so why not educate our children in that way of thinking, in that way of solving problems? Well some have already started to do so. By creating personalised learning environments, in fact, not one size fits all. By fostering collaboration instead of competition, and by promoting a growth mindset instead of a fixed mindset.
Why not transform this classic culture of our education systems to a culture of innovation. We should encourage children to have an entrepreneurial mindset and to deal with the challenges they are going to face in the future instead of just focusing on getting high grades.
Do you know about the education system in Finland? This is something that really impressed me. First of all I would recommend to watch this short video by Michal Moore about it. They decided to stop measuring the statistics in order not to miss the human aspect. Again, human-centered design. And guess what? 66% of students have higher education which is the highest rate in the European Union.
They almost have no mandated standardised tests, no rankings, no comparisons or competitions between students, schools are publicly funded and the level of education is the same for everyone. One of the main focus is to have high level professors. But they spend on average less time in the classroom than in other countries! The children spend much more time playing outside and homework is very very low.
Design thinking at work
Today, competitive advantage is mainly always linked to innovation. And who says innovation says creativity. Creativity is something you train and you need to make room for it. Business leaders don’t need to be creative to get a creative team, but they do need to lead for creativity.
All members of a team should be able to participate to get better solutions. The team spirit should be strong and the culture environment of the company itself should inspire the people. We see many more and more companies trying to get this “startup” culture, where the employee feels like he’s at home while he’s in the office, feels like he’s with his family while he’s with his colleagues.
The typical working space with working hours from 9 to 6 could block your creativity. Having an office where you feel comfortable and where you have different ambients and where you have more flexible hours can be much more inspiring. The idea is to provide benefits to the people, but we’re not only talking about material benefits, it’s more of a lifestyle benefit. Again, human-centered design. A working environment designed focusing on your employee, because if employees are not engaged, I guarantee that you won’t have neither creativity neither innovation.
Last few tips about design thinking
What I can say is that giving power to the people is primordial. You shouldn’t wait to get a perfect result and then show it. You should use your intuition and work on getting fresh ideas, regularly, learn how to prototype rapidly and try things out, at a low costs. Be quick, do it quickly and show it quickly.
Always look for feedback, try to know what they think and how they feel about it. Iterate, do it again and again. Being wrong is not a problem and having bad ideas even less. Look at it differently, it will help you get to the next phase and then again to the next one. You won’t get it the first time, and if you do, let’s just say you were lucky! You need to prototype and test to fail, to understand why you fail and to fix it, always trying to get closer to the final goal. You fail quickly and cheaply in order to succeed.
Focus on your user and focus on constant innovation.










2 Comments
Luisadub
whoah this blog is great i love reading your posts. Keep up the great work! You know, a lot of people are looking around for this information, you can aid them greatly.
JaimeJah
Good post! I read your blog often and you always post excellent content. I posted this article on Facebook and my followers liked it. Thanks for writing this!